Here’s the bottom line: a copay is a fixed fee paid at each provider visit, while a deductible is the cumulative out-of-pocket amount you must reach annually before your insurer shares costs. Understanding these distinctions allows you to optimize routine cash flows and safeguard capital against unexpected medical expenses.
Essential Comparison Of Copay And Deductible

| Feature | Copay | Deductible |
|---|---|---|
| Trigger Point | Per service visit | Annual threshold |
| Payment Type | Fixed ticket-like fee | Cumulative costs |
| Impact On Cash Flow | Predictable small outlay | Deferred yet potentially sizable |
In high-net-worth planning, select a copay structure for steady budgeting when you anticipate frequent consultations. Opt for a deductible design if you can maintain liquidity buffers and prefer lower annual premiums.
“If you schedule monthly executive check-ins, secure small copays. If you can absorb larger occasional bills, position yourself with a higher deductible.”
– Expat Insurance Advisor
Understanding How Copay And Deductible Work
Think of each copay as a fixed airport security fee—immediate and certain. Your deductible resembles an annual lounge-membership threshold: once achieved, coverage escalates significantly.

Building Your Mental Model
- Ticket Fee: A defined copay at every GP or specialist appointment.
- Annual Barrier: The deductible you meet before coinsurance applies.
- Premium Trade-Off: Lower deductibles correlate with higher premiums, and vice versa.
Common Misconceptions
Copays often run independently of deductibles—even after crossing the annual threshold, you may still owe copays on routine visits. Always verify policy language to prevent unwelcome surprises during critical treatments.
Explore how excess charges and deductibles intersect in Spotting the Fine Print Excesses and Deductibles.
Projecting Your Out-Of-Pocket Exposure
- Tally expected GP and specialist visits × copay.
- Estimate diagnostic and procedure costs that feed into the deductible.
- Include coinsurance percentages post-deductible.
For example, a plan with $25 copays and a $500 deductible can exceed the cost of a $0 copay plan with a $2,000 deductible if you average more than 20 visits per year.
“High deductibles reduce premiums by up to 30% but require disciplined liquidity reserves for emergencies.”
– IPMI Strategy Expert
Understanding Coinsurance Interplay
After satisfying the deductible, many plans switch to coinsurance:
- 10% for inpatient stays
- 20% for outpatient specialties
- 30% in aggressive premium-reduction designs
High-net-worth clients often cap coinsurance at 20% to maintain predictable cost-sharing while still negotiating lower premiums.
Comparing Cost Sharing In IPMI Policies
For discerning expats, regional nuances shape copay and deductible frameworks.
Regional Variations
- Europe: Copay caps per visit; routine costs are contained.
- Asia: Small deductibles followed by coinsurance blends.
- Americas: Elevated annual deductibles; premium relief in exchange for upfront risk.
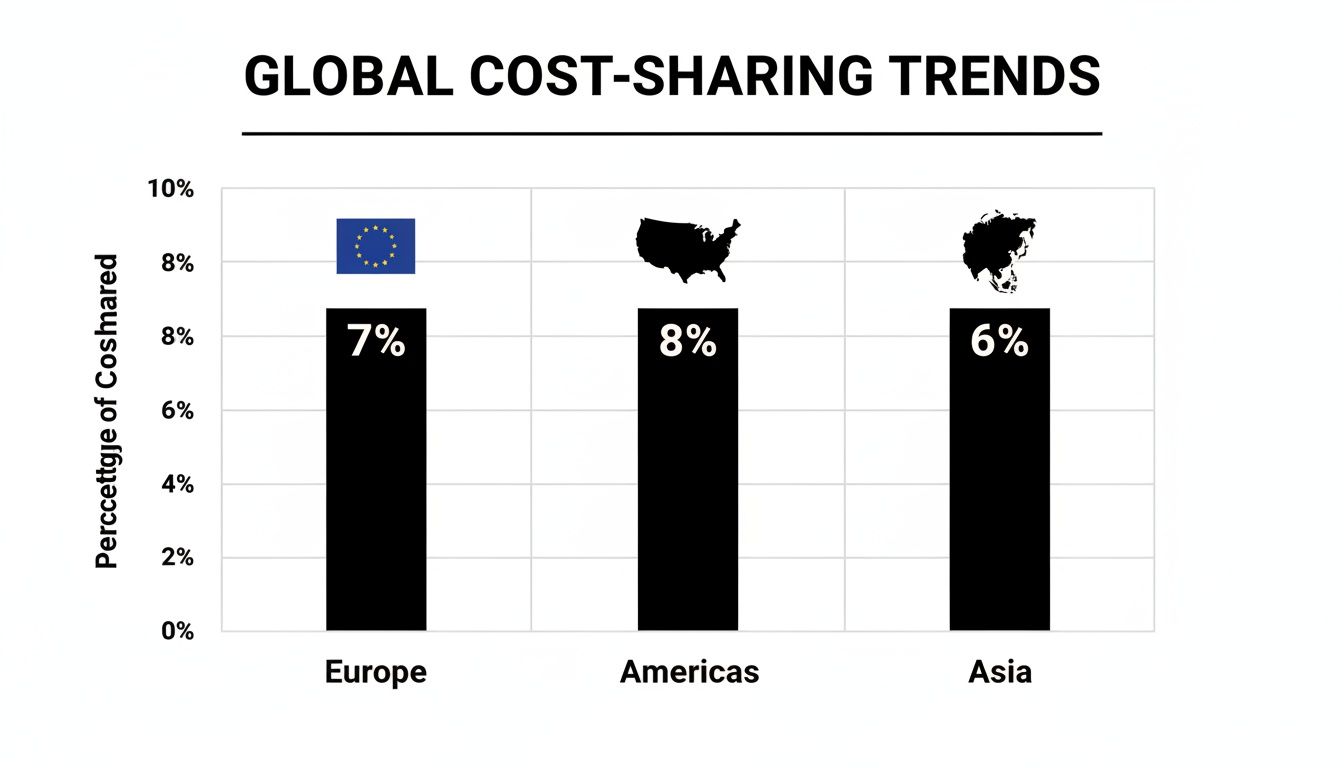
Amid an 8.5% global medical inflation trend, 59% of US employers aim to increase cost-sharing next plan year. Learn more about cost containment on Mercer’s site
| Region | Medical Trend (%) | Primary Cost-Sharing Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Europe | 7% | Copay Caps |
| Americas | 8% | High Deductibles |
| Asia | 6% | Coinsurance Blends |
Design Insights
- Copay Limits: Constrain routine outlays.
- Annual Deductibles: Discourage minor claims.
- Coinsurance Tiers: Share larger-claim risk.
Negotiate referral waivers for primary-care to sidestep full deductibles on in-network care. Preauthorisation checkpoints also streamline major procedure approvals—learn more in our preauthorisation and direct settlement guide.
Expat Cost Scenarios
This section models three profiles—single executive, family of four, retired couple—revealing real-world out-of-pocket narratives.
Single Executive Worksheet
Monthly premium: $1,200
Deductible options: $500 or $2,000
Copays: $30 GP, $60 specialist; 10% coinsurance inpatient
- GP: 8 visits × $30 = $240
- Specialist: 4 × $60 = $240
- Tests: 2 × $50 = $100
Total out-of-pocket:
• $500 deductible: $1,080
• $2,000 deductible: $2,240
“High deductibles can reduce premiums by 20%, but you need a robust liquidity buffer.”
– IPMI Advisor
Family Of Four Projection
Monthly premium: $3,500; $1,000 deductible; $25 copays
| Scenario | Deductible | Total OOP | Premium Adjustment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | $1,000 | $1,600 | – |
| Elevated | $5,000 | $5,600 | –25% |
Additional metrics: average individual deductible in US employer plans is $1,886 (up 17% over five years); average family premium is $26,993 with worker contributions of $6,850 (up 43% in a decade). Learn more about these trends in the 2025 survey
Retired Couple Analysis
Monthly premium: $2,000; $1,500 deductible; $20 copays
Assumptions: 2 specialists, 1 test, 1 emergency stay costing $7,000
- Routine visits: 3 × $20 = $60
- Deductible: $1,500
- Emergency: $5,500 × 10% = $550
Total OOP: $2,110 vs. $24,000 annual premiums (8.8% risk ratio).
“Retirees must balance lower copays with sufficient reserves for hospital bills.”
– Expat Health Consultant
Premium Impact And Claim Flow
Adjusting deductibles by $1,000 often trims premiums ~15%. Globally, out-of-pocket contributions rose to 20% of health spending across 126 countries in 2022 (OECD, WHO). In the US, 36% of adults delay care due to costs; in Europe, capped copays keep that below 4%.
Claim Adjudication Process
- Submit itemized bills.
- Insurer audits coverage.
- Copays and deductibles are deducted.
- Remaining balance is paid or reimbursed.
Avoid bottlenecks: adhere to preauthorisation protocols and direct settlement guidelines (preauthorisation and direct settlement).
Negotiation And Selection Tactics
Benchmark quotes from at least three IPMI providers:
- Obtain full premium breakdown by copay/deductible tier
- Insist on emergency vs. routine scenario analyses
- Review detailed coinsurance tables
- Request cash-flow projection charts
Secure preventive-care waivers for $0 copays on annual wellness exams, vaccinations, telehealth and lab tests. Each waiver can save $200–$300 annually.
Structuring Tiered Deductibles
| Tier | Service Type | Deductible Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Care | GP visits | $250 |
| Specialist | Consultations | $500 |
| Inpatient | Hospital stays | $3,000 |
Captive Arrangements And Self-Insurance
High-net-worth clients may form captives or self-insure overlays to retain underwriting gains, access reinsurance, and secure tax efficiencies. A group of finance professionals saw a 15% rebate after two claim-free years.
FAQ
What Are The Trade-Offs Between Low Copays And High Deductibles?
Low copays yield predictable per-visit costs but higher premiums; high deductibles lower premiums yet demand greater liquidity.
How Do You Model Worst-Case Scenarios?
Perform a stress test: estimate maximum annual claims, apply coinsurance, and compare OOP exposures under each deductible tier.
Which Negotiation Levers Yield Biggest Savings?
Preventive-care waivers and tiered deductibles can cut premiums by up to 20%.
For policy terms definitions, see our guide to expat medical insurance policy terms.
Ready to optimize your copay and deductible balance? Schedule your private consultation: Schedule Your Consultation

