For the discerning individual relocating to the United States, navigating its healthcare system is a primary and critical task. Securing premier medical insurance is not merely a sensible precaution for foreigners in the USA—it is an absolute necessity for the preservation of your financial portfolio.
Unlike many countries with state-funded healthcare, the U.S. system is a distinct landscape dominated by private enterprise. This structure means a single, unforeseen medical event can result in liabilities of a magnitude that may be difficult to comprehend. Without meticulously selected coverage, you are financially exposed to a degree you have likely never previously experienced.
Why US Medical Insurance Is a Non-Negotiable Asset

To view American medical insurance as a simple monthly expenditure is a profound miscalculation, particularly for those accustomed to a high degree of financial security. It is not an expense; it is an indispensable asset protection strategy.
A single hospitalization or one significant medical procedure can readily generate invoices extending into the hundreds of thousands of dollars. This is not hyperbole. An unexpected health issue can precipitate a full-scale financial crisis, posing a direct threat to your savings, investments, and your family's legacy.
Superior insurance acts as a financial firewall. It shields your personal assets from the exceptionally high costs of U.S. healthcare, allowing you to focus on the matter of genuine importance: your recovery. This is especially true in a market where costs are not only high but are also on a consistent upward trajectory.
To provide perspective, the U.S. health insurance market is a colossal economic force, projected to surge from approximately USD 613 billion to over USD 1.2 trillion by 2034. For any individual new to the country, this staggering growth underscores a simple truth: medical care here is exceptionally expensive. Private insurance is your essential safeguard against that risk. You may review further details about these market projections to understand the implications for consumers.
Essential US Health Insurance Terms at a Glance
Before we proceed, it is important to familiarize yourself with the requisite terminology. The lexicon of U.S. health insurance can be extensive. This reference table distills the most common terms you will encounter in any U.S. health insurance policy.
| Term | What It Means for You | Practical Example |
|---|---|---|
| Premium | Your fixed monthly payment to maintain active insurance coverage. This is paid regardless of medical service utilization. | You remit $500 every month to the insurance company. |
| Deductible | The amount you must pay out-of-pocket for covered services before your insurance begins its financial contribution. | Your plan has a $2,000 deductible. You are responsible for the first $2,000 of your medical expenses for the year. |
| Copayment (Copay) | A fixed fee you pay for a specific service, such as a physician consultation, after your deductible has been met. | Your plan specifies a $30 copay for a specialist visit. After meeting your deductible, you pay $30 for each such visit. |
| Coinsurance | The percentage of costs you share with your insurer for a covered service after your deductible has been met. | Your plan features 20% coinsurance. After meeting your deductible, for a $1,000 invoice, you pay $200 (20%) and the insurer pays $800 (80%). |
| Out-of-Pocket Maximum | The absolute maximum amount you will pay for covered services in a plan year. Upon reaching this limit, the insurer covers 100% of subsequent approved costs. | Your out-of-pocket maximum is $8,000. Once your combined expenditures (deductibles, copays, coinsurance) reach $8,000, you have no further liability for covered care that year. |
| Provider Network | The roster of physicians, hospitals, and clinics with which your insurance plan has negotiated rates. Remaining "in-network" is paramount for cost control. | Your plan is a PPO. A consultation with an in-network physician costs a $30 copay. An "out-of-network" visit could result in you being liable for 50% of the total bill. |
Acquiring a firm grasp of these core concepts is the foundational step. They are the structural components of every policy and dictate your ultimate financial liability when you require care.
Key Insurance Categories to Consider
The appropriate category of insurance is contingent upon the duration and purpose of your stay. The market is segmented into distinct categories, each engineered for a different type of visitor or resident. Selecting correctly is of fundamental importance.
The primary categories are:
- Short-Term Visitor Insurance: This is suitable for tourism, business engagements, or any brief visit. It is designed for acute emergencies, such as accidents or sudden, severe illnesses, and does not cover routine or preventive care.
- International Student Insurance: Tailored specifically for individuals on F-1 or J-1 visas, these plans must satisfy stringent requirements mandated by academic institutions. They offer far more comprehensive benefits than a standard visitor plan.
- Global Expatriate Plans: These are the premier, long-term policies ideal for professionals, executives, and families residing in the U.S. for a year or more. They provide extensive benefits, frequently including worldwide coverage, wellness programs, and access to elite physicians and hospitals.
The most critical distinction to make is between coverage designed for temporary emergencies and a robust plan built for sustained, high-quality care. A simple travel policy is insufficient for anyone planning a significant stay in the United States.
Selecting the appropriate plan is not only about healthcare; it is about compliance and securing peace of mind. It ensures you satisfy any visa stipulations while providing confidence that you can access world-class medical care without liquidating your assets. In the following sections, we will detail the process of aligning your visa status with the correct insurance and help you decide between a domestic U.S. plan and a global expatriate policy.
Matching Your Visa Status to the Right Insurance Plan
Procuring the right medical insurance for foreigners in USA is not a universal solution. The single most significant factor shaping your options is your legal status in the country, specifically your visa classification and intended length of stay.
Your visa acts as the key that unlocks specific tiers of the U.S. insurance market. A discrepancy between your visa and your insurance can lead to compliance issues, significant coverage gaps, or catastrophic, unforeseen liabilities.
Each visa category is purpose-driven, and the insurance industry has developed products to correspond. The policy ideal for a short-term business visitor would be entirely inadequate for a skilled professional relocating their family for several years. Therefore, the initial step is to attain absolute clarity on your immigration status, as it dictates not just what you can purchase, but what will provide the necessary level of protection.
Insurance For Students And Exchange Visitors
If you are entering the U.S. on an academic or exchange visa, such as an F-1 or J-1, your insurance decision is often predetermined. American universities and program sponsors impose strict, non-negotiable insurance regulations as a condition of enrollment.
These are not mere suggestions. They often mandate high policy maximums, low deductibles, and specific coverage for services like medical evacuation and repatriation of remains.
- University-Sponsored Plans: Most institutions offer their own group plans guaranteed to meet their requirements. While convenient, it is prudent to compare their cost and benefits against options available on the private market.
- Private Student Plans: You can also procure specialized plans from private insurers engineered to meet or exceed standard F-1 and J-1 requirements. These can sometimes represent a superior value proposition.
Be advised: failure to secure a compliant policy can jeopardize your academic standing and visa status. You must obtain the precise requirements from your institution and ensure every criterion is met.
Coverage For Skilled Workers And Expatriates
Foreign professionals arriving on employment-based visas, such as the H-1B for specialty occupations or the L-1 for intracompany transfers, face a different set of considerations. You are typically relocating for an extended period, often with family, and thus require comprehensive, long-term health coverage.
The most prevalent solution is an employer-sponsored group health plan. A top-tier health insurance package is a key component of how U.S. corporations attract global talent. These plans are generally equivalent to those offered to American employees, covering a full spectrum of care from routine check-ups to major surgical procedures.
Managing the administrative tasks associated with relocation can be demanding. For immigration matters, many professionals utilize tools like the top immigration case management software to maintain organization.
For professionals and their families, an employer's plan is often the gold standard. However, an international expatriate policy can offer superior global portability—a feature we will explore in greater detail.
Options For Visitors And Those On The Path To Residency
For short-term visits, such as tourism or business meetings on a B-1/B-2 visa, a standard visitor or travel medical plan is appropriate. These policies serve as a safety net for unexpected accidents or illnesses and are not intended for routine care or pre-existing conditions.
Conversely, if you are on a definitive path to permanent residency (a "green card"), your insurance strategy will evolve. You might begin with a long-term expatriate plan, but upon obtaining permanent residency, you become eligible for the same domestic insurance options as U.S. citizens, including plans offered on the ACA Marketplace.
This transition is significant, opening a new range of choices. If you are evaluating your long-term options, our guide on choosing the right expat medical insurance policy offers valuable insights to inform your decision.
Domestic US Plans vs. Global Expatriate Coverage
When arranging medical insurance in the USA as a foreign national, you will encounter a significant decision point. Do you opt for a domestic US plan or a specialized global expatriate policy? This is not a minor detail; it is a strategic choice that will define your healthcare access, financial exposure, and freedom of movement.
The two options are built on entirely different philosophies. One is designed for a stationary lifestyle, the other for a globally mobile one.
The Core Difference: Global Portability
The single greatest distinction is coverage geography. This is what separates a localized plan from a truly global one.
Domestic plans, such as those from the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Marketplace, are designed for U.S. residents. They are geographically rigid; their networks and benefits are almost exclusively confined to the United States. The moment you travel internationally, that financial protection vanishes. For anyone who travels frequently for business, maintains strong connections in their home country, or has global travel aspirations, this is a profound limitation.
International expatriate plans, by contrast, are engineered for this precise lifestyle. They offer a borderless approach to medical care, providing seamless coverage not only in the U.S. but wherever your life or business takes you. This means you are covered whether you are on a business trip to London, visiting family in Singapore, or vacationing anywhere else in the world.
This visual breakdown highlights some of the key differences you’ll find when comparing these two paths.
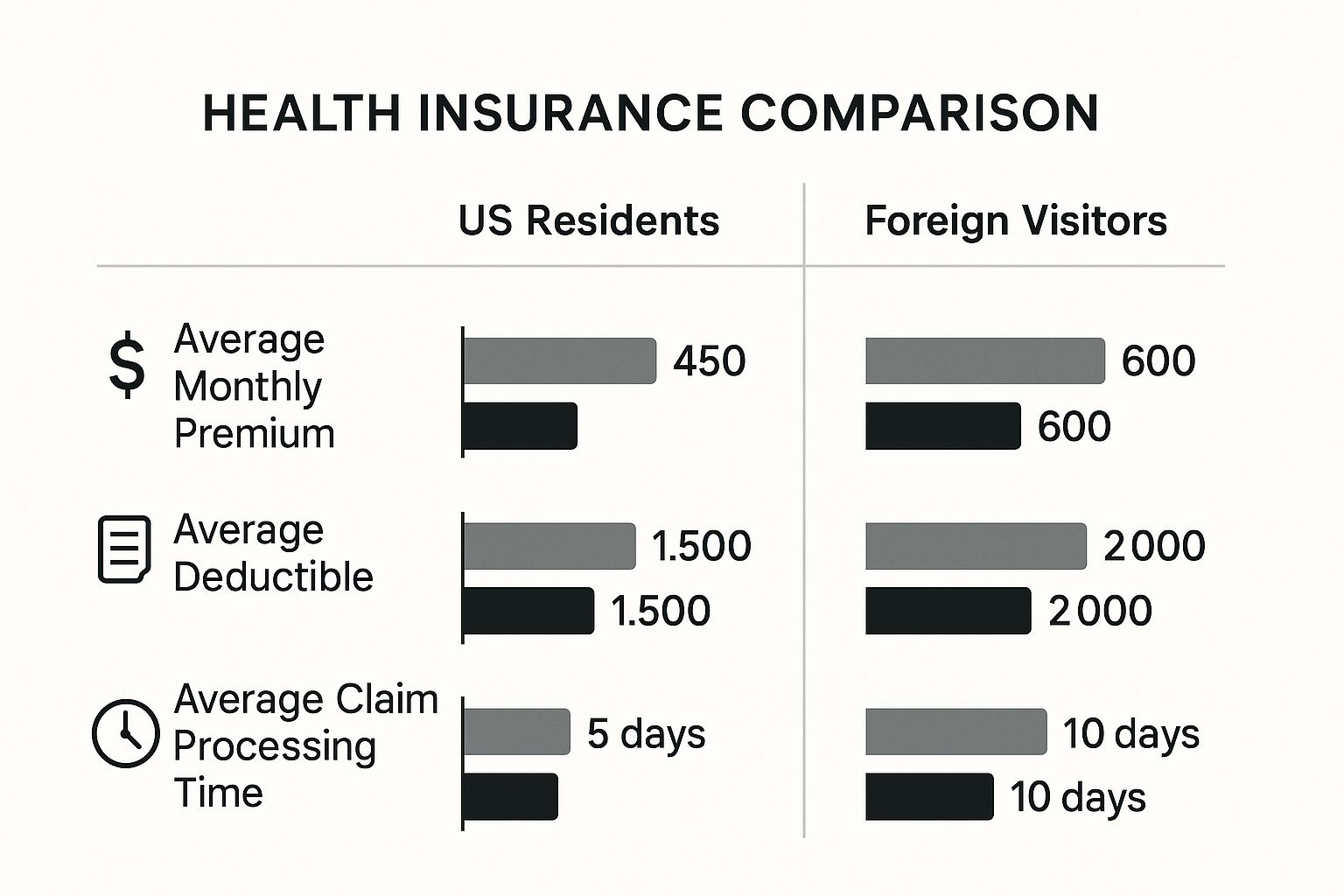
As illustrated, while an expatriate plan may present a higher initial premium, you are acquiring a much broader scope of access and services built for a global life.
To clarify this choice, let's examine the practical differences side-by-side. The table below compares how each type of plan addresses the features that matter most to international professionals.
Comparing Domestic and International Insurance Plans
| Feature | Domestic US Health Plan (e.g., ACA) | International Expatriate Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Primarily within the USA; very limited or no international coverage. | Worldwide, often including your home country. |
| Provider Network | Large network, but confined to the US (and often a specific state). | Curated global network of elite doctors and hospitals. |
| Direct Billing | Common within the US network. | A key feature; insurer pays hospitals directly, worldwide. |
| Medical Evacuation | Not included. An expensive, out-of-pocket catastrophe. | Standard benefit, often worth hundreds of thousands of dollars. |
| Enrollment Period | Strict annual Open Enrollment period. | Flexible, year-round enrollment. |
| Best For | Long-term US residents who do not travel internationally. | Expats, global citizens, and frequent international travelers. |
This comparison demonstrates that your decision is highly dependent on your lifestyle. A domestic plan is sufficient for a life centered in the U.S., but an international plan is an essential tool for anyone living, working, or traveling across borders.
Provider Networks and Direct Billing
Let’s discuss access to physicians and hospitals. Domestic plans from major insurers like UnitedHealth Group or Elevance Health certainly offer extensive provider networks within the U.S. However, a top-tier expatriate plan often provides something different: access to a more curated global network of elite medical facilities and specialists.
More importantly, international plans excel at direct billing. This is a service wherein the insurance company settles the invoice directly with the hospital, regardless of your location worldwide. It is a white-glove service that prevents you from having to pay a substantial hospital bill out-of-pocket during a medical crisis and then seek reimbursement. This feature is a game-changer.
A premier global plan acts as your financial advocate, handling complex international billing procedures so you can focus solely on your health. Domestic plans simply lack the infrastructure to offer this level of service outside of the US.
Emergency Services and Enrollment Flexibility
The included benefits often reveal the intended client for the plan. International policies almost invariably include features that are non-negotiable for a global citizen but are absent from standard domestic plans.
These critical benefits include:
- Medical Evacuation: This covers the staggering cost of transporting you to the nearest center of medical excellence if local care is inadequate. It is a benefit that can be life-saving and prevent financial ruin.
- Repatriation: This covers the costs of returning you to your home country for treatment or, in a worst-case scenario, covers arrangements for the return of remains.
- Home Country Coverage: This ensures you remain fully insured even when visiting your country of origin.
Finally, the rules for enrollment are fundamentally different. Domestic ACA plans are constrained by strict Open Enrollment Periods. If you miss this annual window, you cannot purchase a plan unless you have a specific Qualifying Life Event.
In stark contrast, most international expatriate plans offer year-round enrollment. This grants you the flexibility to secure coverage precisely when you need it—a crucial advantage for anyone relocating on a timeline that does not align with the U.S. government's calendar. This flexibility, combined with their global nature, makes expatriate plans an exceptionally powerful tool for foreigners in the U.S.
Understanding the True Cost of Your US Medical Coverage

Here is a reality many foreigners discover only after arriving: acquiring premier medical insurance for foreigners in usa is not a simple retail transaction. It is a significant financial decision, and the monthly premium is merely the initial component of the total cost. The complete financial picture is a more complex equation.
To truly understand your investment, you must look beyond the premium and become fluent in the core mechanics of your policy: the deductible, copayments, coinsurance, and the most critical figure of all, the out-of-pocket maximum. These elements work in concert to define your total financial risk for the year.
Consider an analogy: purchasing a fine automobile. The base price secures the vehicle, but the final cost is determined by the engine specification (your coverage level), the navigation system (your network access), and optional features (riders for specific needs). Every choice impacts the final number.
Deconstructing the Financial Framework
Your premium is the fixed, recurring payment to keep your insurance active. The other costs manifest only when you utilize medical services. Understanding their interplay is key to accurately forecasting your potential expenses.
- Deductible: This is the amount you must pay from your own funds for covered medical care before your insurance company begins to contribute. A higher deductible typically corresponds to a lower monthly premium, but it also increases your initial financial responsibility.
- Copayments & Coinsurance: After you have satisfied your deductible, you will continue to share some costs. A copayment is a fixed fee for a specific service, such as $50 for a specialist consultation. Coinsurance is a percentage of the total bill—for instance, you might be responsible for 20% while your insurer pays 80%.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: This is your financial safety net. It is the absolute most you will be required to pay for covered medical services in a single policy year. Once your combined spending on deductibles, copays, and coinsurance reaches this threshold, your insurer pays 100% of all other approved costs for the remainder of the year.
Your out-of-pocket maximum is arguably the most important number in your policy. It quantifies your worst-case financial scenario for covered medical events, providing a clear ceiling on your liability and protecting your broader assets.
Factors That Shape Your Premiums
Your policy's price is not arbitrary; it is a calculated risk assessment based on several key factors. Insurers analyze these variables meticulously, and even minor adjustments can significantly alter your premium.
It is also important to recognize the broader market forces at play. If you have ever wondered about the annual increase in insurance prices, you can explore our detailed breakdown on why medical insurance premiums rise year after year.
Here are the key personal and policy factors that drive your cost:
- Age and Health Profile: Younger, healthier individuals typically receive lower premiums. Conversely, advancing age or the presence of pre-existing conditions can increase costs, particularly on plans that utilize medical underwriting to determine pricing.
- Coverage Level: A "platinum" plan with extensive benefits and a low deductible will command a much higher premium than a "bronze" plan designed primarily for catastrophic protection.
- Geographic Location: Healthcare costs vary dramatically between U.S. states. A policy in New York City or San Francisco will be priced differently than one in a state with lower prevailing medical costs.
- Policy Limits and Exclusions: The fine print is paramount. Policies with high benefit limits and minimal exclusions, particularly for high-cost treatments, will naturally carry higher premiums. A thorough review of these details is the only way to ensure you are not exposed to unexpected liabilities when you most need your coverage.
By carefully evaluating all these components, you can transition from merely purchasing insurance to making a truly informed, strategic investment in your health and financial security during your time in the United States.
Getting Your Policy: A Step-by-Step Enrollment Guide
Securing premier medical insurance in the U.S. is not an insurmountable challenge, but it does require organization and an understanding of the system's protocols. View it not as a complex ordeal, but as a methodical process. A clear, step-by-step approach ensures no detail is missed, making the journey from application to active coverage smooth and efficient.
The entire process is a sequence of events, beginning with identifying the right plan and culminating with your insurance ID card in hand. Success depends on having the correct documentation prepared in advance and paying close attention to deadlines, which can vary significantly depending on the type of plan you select.
The Documents You'll Need to Apply
Before beginning an application, assemble your documentation. Having these documents scanned and readily available will save considerable time and prevent delays. Insurers must verify your identity, legal status in the U.S., and your residential address.
This is the foundation of your application. A missing document can bring the entire process to a halt.
You will typically need to provide clear, digital copies of these three items:
- A valid passport: This is your primary form of identification.
- A current U.S. visa: This document confirms your legal presence and often dictates your eligibility for specific plans.
- Proof of a U.S. address: A utility bill, a signed lease agreement, or other official correspondence bearing your name and address is sufficient.
Understanding Enrollment Windows and Medical Underwriting
A critical distinction to grasp is timing. U.S. domestic plans, particularly those on the ACA Marketplace, operate on a strict timetable. They feature a limited Open Enrollment Period that occurs only once a year. If you miss this window, you cannot enroll unless you experience a Qualifying Life Event, such as marriage or loss of other coverage.
This is in stark contrast to the medical insurance for foreigners in usa designed for global citizens—international and short-term plans. These plans offer year-round enrollment. That flexibility is a significant advantage, allowing you to obtain coverage precisely when needed, perfectly aligning with your travel or relocation schedule.
Many of these international and expatriate plans involve a process called medical underwriting. This is a confidential health review where the insurer assesses your medical history to determine eligibility and set your premium. It is absolutely crucial to be completely transparent and thorough in this process. Withholding information can invalidate your policy, leaving you without coverage when you need it most.
The Enrollment Process, Step-by-Step
Once you have selected a plan and your documents are prepared, the path to obtaining coverage is straightforward.
- Complete the Application Form: Fill out the form online. Pay meticulous attention to every detail, providing all requested personal, address, and health information.
- Submit Your Documents: Upload the required paperwork—such as your passport and visa—through the insurer's secure online portal.
- Undergo Medical Underwriting: If required, the insurer's team will review your health history. They may contact you with follow-up questions.
- Receive Your Offer and Pay the Premium: Upon approval, you will receive a formal offer with the final premium. You will make your first payment to officially activate the policy.
- Policy Confirmation: After your payment is processed, you will receive all official policy documents, your insurance ID card, and instructions on how to locate providers and utilize your plan.
While most foreign nationals will utilize private plans, some may eventually interact with government programs. In such cases, knowing procedural details like how to fax Medicare forms could become relevant. Following these steps will put you on an efficient and effective path to securing robust medical coverage in the United States.
Navigating State-by-State Differences in Healthcare
Here is a fundamental truth that many foreigners only discover upon arrival in the United States.
There is no single “U.S. healthcare system.”
What you are actually navigating is a patchwork of 50 distinct healthcare markets, one for each state. Each has its own regulations, cost structures, and quality standards. For a high-net-worth individual seeking medical insurance for foreigners in usa, ignoring these differences is not a mere oversight—it is a significant strategic error.
Your entire healthcare experience can be altered simply by crossing a state line.
The reason is that state governments wield considerable authority over their local insurance markets. Some states mandate that all insurance plans cover an extensive range of services. Others adopt a more laissez-faire approach. This creates a vast disparity in the quality and type of insurance available for purchase.
The Impact of Geography on Your Coverage
The state in which you choose to reside will directly influence three critical aspects of your medical insurance: cost, access, and quality. A top-tier expatriate plan that appears excellent on paper may perform very differently from one state to another, simply due to the local physicians and hospitals within its network.
For example, states like Massachusetts or Minnesota are home to a high concentration of world-class medical centers and research hospitals. A premier insurance plan in Boston will grant you access to this exceptional ecosystem of specialists.
In a more rural state with fewer elite facilities, the strength of your plan's network becomes paramount. It is the sole factor ensuring you can receive high-quality care without extensive travel.
The most sophisticated insurance policy is only as good as the medical infrastructure it provides access to. Your primary objective should be to align your chosen plan with a state that not only meets your lifestyle needs but also possesses a world-class healthcare environment.
State Performance and Your Insurance Choice
The quality disparity between states is not anecdotal; it is a well-documented and significant issue. States such as Massachusetts and Hawaii consistently receive high marks for their healthcare system performance. Others, frankly, can present challenges in obtaining timely, high-quality care.
These differences have a pronounced impact on foreign nationals, as the value of your private insurance is directly tied to its local network and its ability to navigate local regulations. It is worthwhile to review state-by-state performance data to appreciate these regional nuances.
This is precisely why you must meticulously scrutinize an insurer's provider directory for your specific area. Before committing, verify that the plan’s network includes the premier hospitals and specialists you would wish to access. Our deep dive into how to evaluate medical networks is essential reading for this step.
An insurer with a weak or sparse network in your state of residence completely undermines the value of your policy, regardless of the premium. Your decision must be as geographically astute as it is financially sound.
Your Top Questions About U.S. Medical Insurance, Answered
Let's be direct: understanding American healthcare can be like learning a new, complex discipline. It is a maze of unfamiliar terms and regulations, especially for those accustomed to a different system.
Here, I will address the most common and critical questions we hear from foreign nationals. My objective is to provide clear, definitive answers so you can make decisions about your health coverage with confidence.
Can I Just Use Travel Insurance for a Long-Term Stay?
This is one of the most prevalent—and most dangerous—misconceptions. The assumption that travel insurance is a substitute for proper health insurance is incorrect. It absolutely is not.
Consider travel insurance as an emergency response kit. It is designed for sudden, unforeseen events like a fractured leg from a hiking accident or an acute illness. It is built for short-term crises, not for the realities of residing in the U.S.
Here is what travel insurance almost never covers:
- Routine physician visits and annual wellness checks
- Care for pre-existing conditions
- Mental health services
- Maternity and newborn care
Critically, travel insurance fails to meet the stringent insurance requirements for many U.S. visas, such as the F-1 for students or the J-1 for exchange visitors. If your stay extends beyond a brief vacation, a proper health insurance plan is non-negotiable. A robust expatriate plan or a domestic U.S. policy is the only responsible course of action.
How Does Insurance Handle My Pre-Existing Conditions?
This is a complex area, and the answer depends entirely on the type of plan you select. The treatment of pre-existing conditions is one of the most significant distinctions between insurance options for foreigners.
Plans purchased through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace are legally mandated to cover pre-existing conditions and cannot charge a higher premium because of them. The challenge, however, is that access to these plans can be difficult for many non-U.S. citizens.
In contrast, most short-term visitor plans and many international expatriate policies view pre-existing conditions very differently. They might exclude coverage for them entirely, impose a "waiting period" of several months before coverage begins, or offer to cover them only in exchange for a substantially higher premium.
It is imperative to be radically transparent about your medical history on your application. Nondisclosure of a condition, while tempting, is grounds for the insurer to rescind your policy. This could leave you personally liable for enormous medical bills precisely when you require assistance most.
How Do I Find Doctors and Hospitals My Plan Actually Covers?
Your access to healthcare is dictated by your plan's provider network. This is the list of physicians, specialists, clinics, and hospitals that have contracted with your insurance company to provide care at pre-negotiated rates.
Every insurer provides an online search tool or directory to locate these "in-network" providers. Make it standard practice to consult this tool before scheduling any appointment.
Remaining "in-network" is the key to managing your costs. You receive the benefit of those negotiated discounts, which can result in substantial savings. If you go "out-of-network," you are entering a financially precarious territory. Your insurer may cover only a small fraction of the bill, or they may deny the claim entirely, leaving you with a staggering invoice. Always verify a provider's network status twice—once with the insurer's directory, and a second time by contacting the provider's office directly.
Navigating these complexities is why expert guidance is invaluable. At Riviera Expat, we specialize in providing clear, objective advice to help you select a premier international medical insurance plan that aligns with your specific needs. Secure your peace of mind by exploring your options with us. Learn more at Riviera Expat.

